Are you preparing for the GMAT? Understanding the quantitative section is crucial for success, and having a comprehensive overview of essential concepts can make all the difference. In this GMAT Cheat Sheet for Quants, we’ll break down the key mathematical concepts and formulas you need to master.
Core Mathematical Foundations
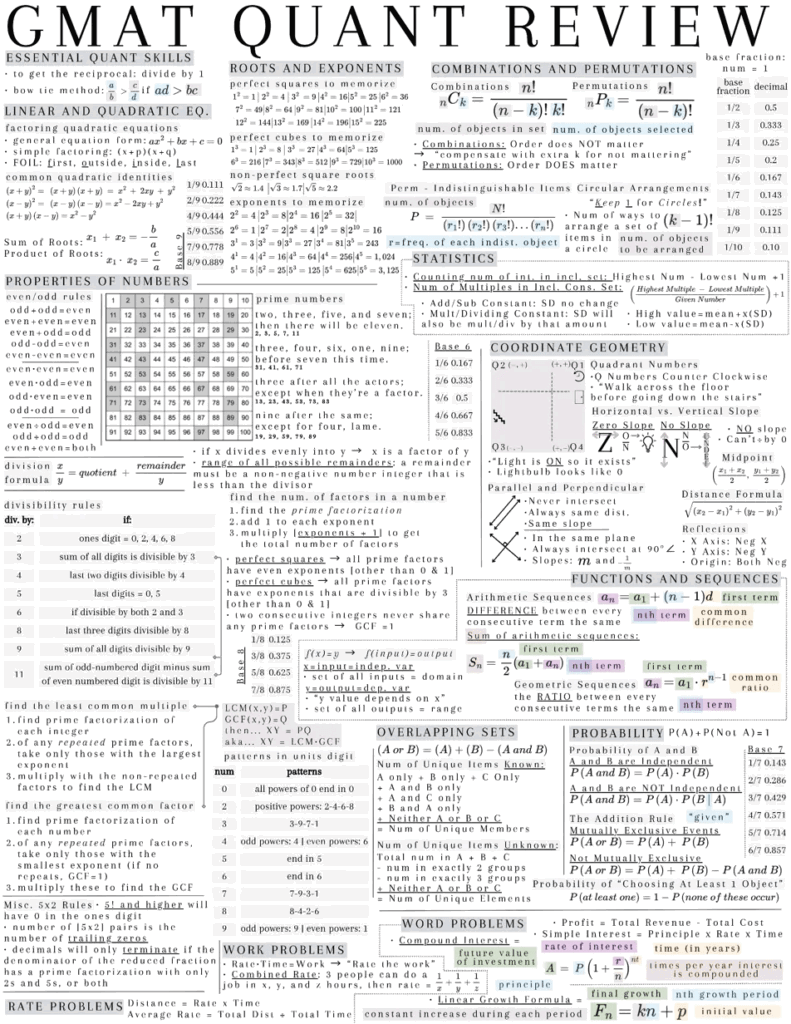
Linear and Quadratic Equations
The foundation of GMAT math starts with understanding how to handle equations. When dealing with quadratic equations, remember the general form:
- ax² + bx + c = 0
- Use the FOIL method: First, Outside, Inside, Last
- For factoring quadratic equations, look for common factors first
Roots and Exponents
Perfect squares and their properties are frequently tested on the GMAT. Key points to remember:
- For any perfect square: i² = 1 if i is odd
- When dealing with exponents, pay attention to negative and fractional exponents
- Common exponential patterns appear in sequences like 2⁴ = 16, 3³ = 27
Combinations and Permutations
Understanding when to use combinations versus permutations is critical:
- Combinations (nCk): Use when order doesn’t matter
- Permutations (nPk): Use when order does matter
- For circular arrangements, use (n-1)! for the number of ways to arrange n objects
Advanced Topics
Properties of Numbers
The GMAT loves testing number properties. Key rules include:
- Even/odd patterns in multiplication
- Divisibility rules (especially for 2, 3, 5, and 11)
- Perfect squares and perfect cubes
- Prime factorization techniques
Statistics Fundamentals
Statistical concepts frequently appear in word problems:
- Mean, median, and mode
- Standard deviation
- Range and quartiles
- Basic probability concepts
Coordinate Geometry
Essential geometric concepts include:
- Understanding slope (rise over run)
- Midpoint formula
- Distance formula
- Parallel and perpendicular lines
Word Problems and Applications
Rate Problems
Remember these key relationships:
- Distance = Rate × Time
- Work problems: Rate × Time = Work completed
- Combined rates require careful attention to units
Overlapping Sets
Set theory appears regularly:
- Understanding unions and intersections
- Calculating unique members in combined sets
- Venn diagram applications
Tips for Success
- Always write out given information
- Draw diagrams when possible
- Check your answers for reasonableness
- Look for patterns in number sequences
- Use estimation techniques for complex calculations
Practice Strategies
The key to mastering GMAT Quant is consistent practice. Focus on:
- Timed practice sessions
- Understanding the underlying concepts rather than memorizing formulas
- Reviewing mistakes thoroughly
- Identifying patterns in question types
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Don’t rush through “easy” questions
- Watch out for unit conversion
- Be careful with negative numbers
- Don’t forget to check for special cases
- Remember to consider all possible solutions
Remember, success in GMAT Quant isn’t just about memorising formulas—it’s about understanding how to apply them in various situations. Practice regularly, focus on understanding concepts deeply, and approach each question methodically. But keep this GMAT Cheat Sheet handy and feel free to return whenever you need to refer to certain formulas!
Note: This guide serves as a reference. Make sure to practice with official GMAT materials and time yourself to simulate actual test conditions.
